First and foremost let me wish all my readers a VERY HAPPY AND SAFE NEW YEAR.
May this year bring abundance of everything in life.
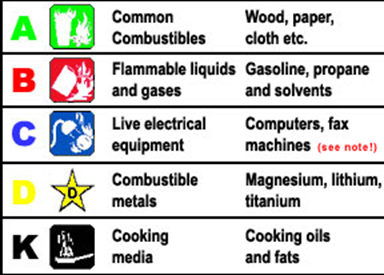
Though Happiness is very important at the same time Safety is very much necessary as it is the only thing that can help us stay alive and injury free. I hope my blogs are helping you all gain knowledge on fire safety and making your homes and work place fire free. In my last blog we have discussed the classification of fire based on the fuel or the substances which can burn. Here we discuss the media or material available to combat and extinguish fire.
They are as follows.
1. WATER : Since time immemorial water has always been used for fire fighting. One of the most natural fire fighting media and available everywhere. Due to its natural property of absorption of heat it is a very effective in fire fighting. Though very effective it can be only used to extinguish Class A Fire IE Fire on Combustible Solids. It cannot be used on the other the other Classes. For example when you use it on Liquid Fires the density of water is more and thereby it increases the fire. Even a drop of water when used on flammable metals can cause explosion.
2. Mechanical and Chemical Foam: This media is widely used on Class B liquid fires. The Foam falls on the surface of the liquid fire like a blanket and cuts off the oxygen supply thereby extinguishing fire. The Foam even cools the liquid to prevent reoccurrence of the fire due to heat. There are different types of foam available and would be too technical and elaborate to explain here.
3. Dry Chemical Powder : There are 3 widely used dry chemical powders for fire fighting.
a. Sodium Bi Carbonate,
b. Mono Ammonium Phosphate and
c. TEC – Ternery Eutectic Chloride.
Sodium Bi carbonate can be used on Classes B and C fires that is fire on flammable liquids, gases and electrical fire. Mono Ammonium phosphate powder which is known as ABC powder can be used on Solids, Liquids, Gas and Electrical fire and hence it is very popular as a fire fighting media. TEC powder is only used for Class D metal fire. All the powders employ the method of Blanketing or Smothering to put out fire. Even though they are very good at fire fighting they however damage the equipments when used on sophisticated and expensive equipments like servers.
4. Carbon di oxide or CO2 : As we all know removal of oxygen cuts off fire and what better material than CO2 to do the job. CO2 is also a very popular agent to extinguish fire on Electrical equipment and most importantly the sophisticated and expensive ones. CO2 is not only used in extinguishers but also used in large automatic fire fighting systems as a Flooding agent. Though very good at putting out fire on electrical equipments it can be used on Liquid and Gas fire too.
5. WET CHEMICAL : This a new recent addition to fire fighting to specifically address the issue of fire on Fatty oils and saturated fats. As grease accumulates when there is combustion, to fight the same a special effect called Saponification is needed. Even Sodium Bi Carbonate has this effect too but of late research has found that wet chemicals are more effective. As there is a growing need for environmental protection there is extensive research going on in the field of fire fighting and new products are being developed. I will talk more about them in my subsequent blogs and writing.Till then read, ruminate and post your doubts and queries on the blog page itself.
Take care and have a great year everyone.
Seshadri Varadrajan.9840814353.
For videos on first aid tune and subscribe to LIVE AND LET LIVE